Singleflight 示例一:基础用法
多次请求共享一次请求的结果
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"golang.org/x/sync/singleflight"
)
func main() {
var group singleflight.Group
// A function that simulates an expensive operation
expensiveOperation := func(key string) (interface{}, error) {
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second) // Simulate delay
return fmt.Sprintf("Result for %s", key), nil
}
key := "unique-key"
// Start multiple goroutines that call the expensive operation through singleflight
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
go func(id int) {
result, err, shared := group.Do(key, func() (interface{}, error) {
return expensiveOperation(key)
})
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Goroutine %d received error: %v\n", id, err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Goroutine %d received result: %v (shared: %v)\n", id, result, shared)
}
}(i)
}
// Wait for goroutines to finish
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
}
输出
Goroutine 0 received result: Result for unique-key (shared: true)
Goroutine 2 received result: Result for unique-key (shared: true)
Goroutine 1 received result: Result for unique-key (shared: true)
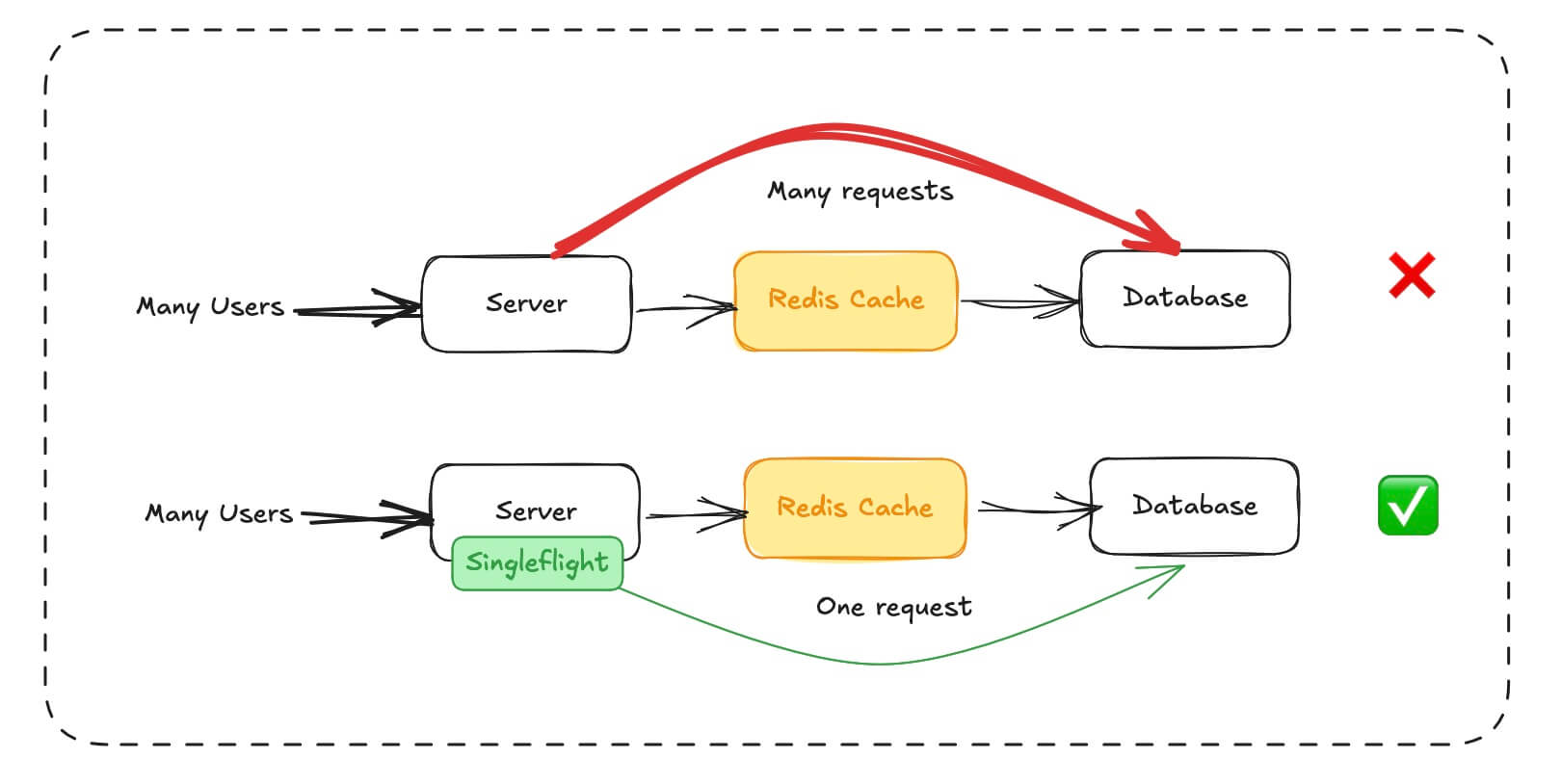
Singleflight 示例二:解决缓存击穿
这个示例集成了数据库、缓存和 HTTP API,有以下几个关键点:
- 提供了
[GET] /gold/prcie和[POST] /gold两个接口模拟黄金价格的更新与查询 - 缓存由更新接口在更新数据后设置失效,由查询接口负责构建
- 高并发查询场景,缓存失效的一瞬间,面临多个请求会同时访问数据库,即缓存击穿
- 高并发查询场景,使用 Singleflight 避免缓存击穿
- 查看访问数据库的次数,看到 Singleflight 在这个场景中的重要作用
创建表作为数据源
-- 创建表
CREATE TABLE gold_realtime_prices (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
price NUMERIC NOT NULL,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
-- 插入一条模拟数据
INSERT INTO gold_realtime_prices (price) VALUES (575.25);
代码示例
通关环境变量设置 enable 来开启、关闭 Singleflight 功能,并发查询和定时更新会自动模拟,启动运行即可
package main
import (
"bytes"
"database/sql"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"os"
"sync"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/go-redis/redis/v8"
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"golang.org/x/sync/singleflight"
)
var (
ctx = context.Background()
rdb *redis.Client
db *sql.DB
sf singleflight.Group
mu sync.Mutex
cacheKey = "gold_price"
visitKey = "visit_times"
queryKey = "query_times"
enable bool
)
func init() {
// 从环境变量中获取 SFL_ENABLE 的值
enableEnv := os.Getenv("SFL_ENABLE")
if enableEnv == "1" {
enable = true
} else {
enable = false
}
}
func initDB() error {
var err error
connStr := "postgresql://<pg-user>:<pg-passwd>@localhost:5432/<dbname>?sslmode=disable"
db, err = sql.Open("postgres", connStr)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return db.Ping()
}
func initRedis() {
rdb = redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{
Addr: "localhost:6379",
DB: 3, // 注意数据库使用的 DB3
})
}
func getGoldPriceFromDB() (float64, error) {
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond) // 增加数据库查询时间 200 毫秒
var price float64
err := db.QueryRow("SELECT price FROM gold_realtime_prices ORDER BY updated_at DESC LIMIT 1").Scan(&price)
return price, err
}
func withoutSingleFlight() (string, error) {
// 查询数据库次数
rdb.Incr(ctx, queryKey)
price, err := getGoldPriceFromDB()
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
priceStr := fmt.Sprintf("%.2f", price)
// 更新缓存
rdb.Set(ctx, cacheKey, priceStr, time.Hour)
return priceStr, nil
}
func withSingleFlight() (string, error) {
v, err, _ := sf.Do(cacheKey, func() (interface{}, error) {
// 查询数据库次数
rdb.Incr(ctx, queryKey)
price, err := getGoldPriceFromDB()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
priceStr := fmt.Sprintf("%.2f", price)
// 更新缓存
rdb.Set(ctx, cacheKey, priceStr, time.Hour)
return priceStr, nil
})
if err != nil {
return "", errors.New("could not get price")
}
return fmt.Sprintf("%.2f", v), nil
}
func getGoldPrice(c *gin.Context) {
// 接口调用次数
rdb.Incr(ctx, visitKey)
price, err := rdb.Get(ctx, cacheKey).Result()
if err == redis.Nil {
if enable {
v, err := withSingleFlight()
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "could not get price"})
return
}
price = v
} else {
v, err := withoutSingleFlight()
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "could not get price"})
return
}
price = v
}
} else if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "could not get price from cache"})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"price": price})
}
func updateGoldPrice(c *gin.Context) {
var request struct {
Price float64 `json:"price"`
}
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&request); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"error": "invalid request"})
return
}
// 更新数据库中的价格
_, err := db.Exec("INSERT INTO gold_realtime_prices (price, updated_at) VALUES ($1, NOW())", request.Price)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{"error": "could not update price"})
return
}
// 使缓存失效
rdb.Del(ctx, cacheKey)
c.Status(http.StatusNoContent)
}
func main() {
if err := initDB(); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
initRedis()
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/gold/price", getGoldPrice)
r.POST("/gold", updateGoldPrice)
// 启动一个协程,并发调用 /gold/price 接口
go func() {
simulatedAccess()
}()
// 启动一个协程,并发调用 /gold 接口
go func() {
simulatedUpdate()
}()
if err := r.Run(":8080"); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func simulatedAccess() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
startTime := time.Now()
for time.Since(startTime) < 6*time.Second {
go func() {
resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8080/gold/price")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error making GET request:", err)
} else {
body, _ := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
fmt.Println("Response from /gold/price:", string(body))
resp.Body.Close()
}
}()
time.Sleep(1 * time.Millisecond)
}
}
func simulatedUpdate() {
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
ticker := time.NewTicker(500 * time.Millisecond)
defer ticker.Stop()
startTime := time.Now()
for time.Since(startTime) < 5*time.Second {
<-ticker.C // 等待下一个时间点
// 生成随机价格
price := randomPrice(560.0, 580.0)
// 准备 POST 请求数据
data := map[string]float64{"price": price}
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(data)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error marshalling JSON:", err)
continue
}
resp, err := http.Post("http://localhost:8080/gold", "application/json", bytes.NewBuffer(jsonData))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error making POST request:", err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("Posted price: %.2f, response status: %s\n", price, resp.Status)
resp.Body.Close()
}
}
func randomPrice(min, max float64) float64 {
return min + rand.Float64()*(max-min)
}
运行
# 未开启 SingleFlight
$ SFL_ENABLE=0 go run main.go
# 开启 SingleFlight
$ SFL_ENABLE=1 go run main.go
结果(未开启 Singleflight)

结果(开启了 Singleflight)

可以看出,启用 Singleflight 后,请求数据库的次数等于更新接口调用的次数,缓存失效时,它的机制决定了在并发请求下,它同时只发起一次对数据库的请求,避免缓存击穿
本例使用数据库作为示例,其实 Singleflight 不关心服务要请求的资源是数据库、存储还是三方接口,只要资源有唯一的标识就可以将并发的请求合并为一,在请求有结果时统一返回,特别适合高并发请求资源的场景
除了应对缓存击穿,在高并发请求 Redis 前也可以前置 SingleFlight,将结果共享、进一步降低 Redis 的压力
Singleflight 简单的使用先到这里,That's all.